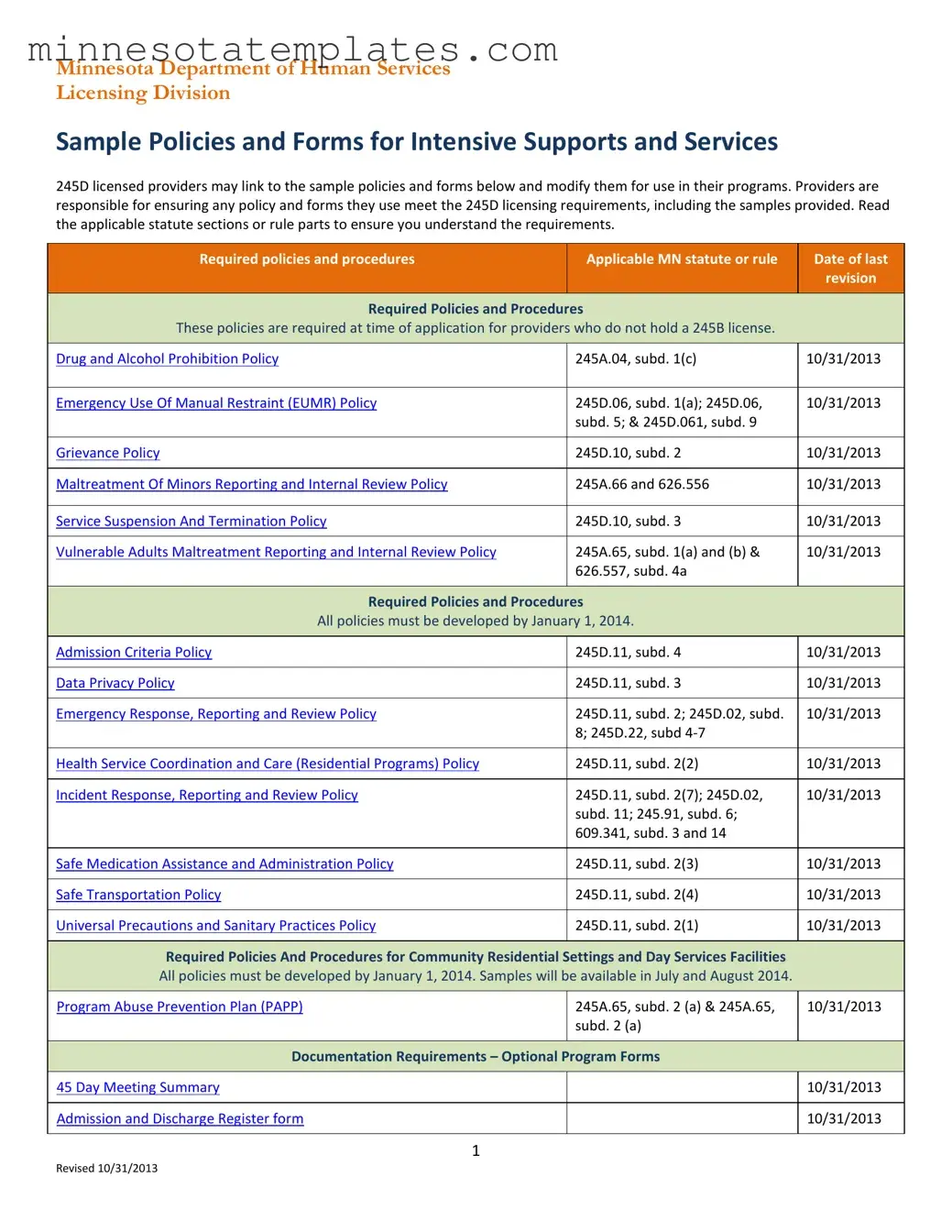
Blank Minnesota Dhs Template
The Minnesota Department of Human Services (DHS) provides a comprehensive framework for 245D licensed providers through its set of required policies and procedures, encapsulated in the Minnesota DHS form. This form serves as a critical resource for providers, detailing essential policies that must be established prior to application, particularly for those not holding a 245B license. Key policies include the Drug and Alcohol Prohibition Policy, Emergency Use of Manual Restraint Policy, and Grievance Policy, each aligned with specific Minnesota statutes. Providers are tasked with ensuring that their policies comply with the outlined licensing requirements. The form also outlines additional required policies, such as those addressing maltreatment of minors and vulnerable adults, service suspension and termination, and health service coordination. Furthermore, the Minnesota DHS form delineates optional program forms and documentation requirements, enhancing the operational standards for intensive support services. Timely adherence to these guidelines is crucial, as all policies must be developed by January 1, 2014, to maintain compliance and ensure the safety and well-being of service recipients.
Key takeaways
When dealing with the Minnesota DHS form, there are several important points to keep in mind. Understanding these can help ensure compliance and streamline the process.
- Know the Required Policies: Familiarize yourself with the specific policies that must be in place, such as the Drug and Alcohol Prohibition Policy and the Emergency Use of Manual Restraint Policy.
- Review Statutes: Read the applicable statutes or rules related to the policies to ensure you fully understand the requirements.
- Timely Development: All required policies must be developed by January 1, 2014. Make sure to prioritize this timeline.
- Modification of Samples: You can link to sample policies and forms provided by the Minnesota DHS and modify them for your program's needs.
- Documentation Matters: Keep track of documentation requirements, including optional program forms like the Admission and Discharge Register.
- Emergency Preparedness: Policies related to emergency response and reporting are crucial. Ensure they are clear and comprehensive.
- Training is Key: Staff orientation and training are essential components of compliance. Utilize the Staff Orientation and Training Packet effectively.
- Continuous Improvement: Regularly evaluate and update your policies and procedures to align with best practices and regulatory changes.
Misconceptions
Understanding the Minnesota Department of Human Services (DHS) form can be crucial for providers. However, several misconceptions often arise regarding its requirements and usage. Here are eight common misunderstandings:
- All policies are optional. Many believe that the policies outlined in the Minnesota DHS form are merely suggestions. In reality, certain policies are mandatory for compliance with the 245D licensing requirements.
- The sample policies cannot be modified. Some providers think they must use the sample policies exactly as presented. However, these samples are intended to be modified to fit the specific needs of each program, as long as they still meet licensing standards.
- Only new providers need to worry about these forms. There is a misconception that only new providers must adhere to these policies. Existing providers must also ensure that their policies are updated and compliant with the latest requirements.
- Deadlines are flexible. Many assume that deadlines for policy development and revision can be adjusted. However, all policies must be developed by the specified deadline of January 1, 2014, to remain compliant.
- All forms are required for every provider. Some think that all forms listed in the DHS document must be completed by every provider. In fact, only certain forms are required based on the specific services offered and the licensing category.
- Policies can be created without understanding the statutes. It is a common belief that providers can develop policies without fully understanding the applicable statutes. However, knowledge of the relevant laws is essential to ensure compliance.
- There is no need for ongoing training. Some providers believe that once they have established their policies, they do not need to provide further training. Continuous training and updates are critical to ensure staff understand and implement these policies effectively.
- Documentation is not important. A misconception exists that documentation of compliance with these policies is not necessary. In reality, thorough documentation is vital for accountability and can be crucial during audits or inspections.
Being aware of these misconceptions can help providers navigate the complexities of the Minnesota DHS form more effectively. Proper understanding and implementation of the required policies and procedures are essential for maintaining compliance and ensuring the well-being of service recipients.
Additional PDF Templates
What Grants Are Available for College Students - Discuss how you will utilize evaluation results to further enhance your initiatives.
Mn Ticket Lookup - The Ifp103 form sets the stage for equitable legal representation.
For anyone looking to navigate vehicle transactions in Alabama, understanding the Motor Vehicle Power of Attorney requirements is vital. This document ensures that you can carry out important tasks regarding motor vehicles without complications, providing peace of mind in the process.
Self Employment Tax Mn - Organizations should ensure all previous losses are reported correctly to maximize deductions.